Insurance companies transfer individual and business risk for a price. They crunch numbers and calculate risk scenarios to develop pricing strategies that balance profits and payouts. Profits allow insurance companies to manage their cash so it’s available when their customers make claims. An insurance company’s ability to pay its debts and claims makes it stable. It’s the reason for buying insurance in the first place.
Credit rating companies also crunch numbers and run data points to see how insurance companies are faring in the economic climate. An insurance company’s financial stability rating gives insight into its solvency. The less financially secure an insurance company is, the higher the risk of financial insolvency, especially after a catastrophic loss.
Even though it’s rare, an insurance company may miss the mark and accidentally saturate its risk portfolio.
Your agent can help you decide which company is best for you
An independent insurance agency is licensed to sell multiple types of insurance from different insurance companies. The more insurance companies an agency works with, the more options for you, the client. They can help match you with insurance companies that will take on your risk.
They can also help you narrow down the options as you decide which coverage best suits your needs. One of the selling points an agent might bring to you is the insurance company’s rating.
Credit rating companies
There are several credit rating agencies for insurance companies, each with a proprietary methodology for rating and analysis. A credit rating company summarizes its opinion on the long-term financial stability of an insurance company by analyzing its ability to pay its claims, debts and other financial obligations. Agents, brokers, investors, regulators, educators and policyholders rely on credit rating companies to make financial recommendations.
According to the Insurance Information Institute (Triple-I), an insurance company might publish the most favorable company rating, omitting less favorable ones. Triple-I suggests comparing two rating companies for a more accurate picture. And check the ratings’ dates to ensure they’re the most recent.
Either way, your insurance company should be financially stable to repay you after a loss; credit ratings provide that financial snapshot.
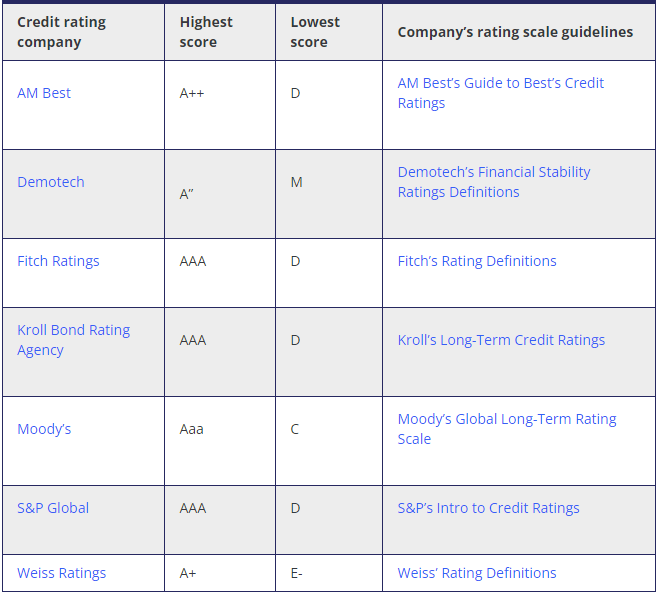
What the credit ratings mean
Most independent agencies will give you recent credit ratings and explain what they mean as part of a quote:
Ways insurance companies manage their risk
Insurance companies must balance the money they receive (premiums) against the cost of losses policyholders might incur during their policy periods (risk).
They use multiple techniques to diversify their risk so they don’t get hit with a windfall of claims and simultaneous payouts. Many companies diversify their finances by offloading higher-risk properties to reinsurance companies or charging higher premiums.
Others may leave a market because the risk is too high, refusing to take on new insurance policies while they recuperate. For example, climate change has forced insurance companies to rethink their financial exposure. Policyholders in areas prone to wildfires, hurricanes or floods have experienced insurers leaving the market or not renewing their policies.
Insurance companies usually have insurance for their insurance portfolio. What they can’t take on alone, they transfer to another company. If they go bankrupt, they rely on the financial backing or their state’s insurance commission to guarantee active policies.
When an insurance company fails
Insurance companies are regulated by the states and exempt from federal bankruptcy law. Evaluating an insurance company in financial distress is a long and complex process. There are many steps before insolvency; most are designed to help the company avoid bankruptcy. They can involve state regulatory oversight and financial risk management assistance called rehabilitation.
Insurance policyholders are guaranteed some coverage for active claims even after an insurance company is declared bankrupt (like FDIC-insured banks). Every state has a guaranty association or fund to assist with claims after a court orders an insurance company to liquidate or file for bankruptcy.
Guaranty funds and associations assist with claims
Guaranty funds and associations protect policyowners (and their beneficiaries) in the policyholder’s resident state. Citizens who live abroad get protection from the guaranty association where the insurance company is located.
The state guaranty association works with regulators and commissioners to pay claimants, answer questions, manage claims data and coordinate the liquidation. An insurance company in liquidation must cancel current policies and cannot issue new policies. They must notify policyholders and direct them to seek coverage elsewhere.
But the issue of active claims remains.
According to the National Conference on Insurance Guaranty Funds, if a state court orders a licensed insurance company to be liquidated or bankrupt:
- State guaranty funds and associations are triggered.
- Active claims are transferred to each state guaranty for review and payment.
- Claims are paid from a pool of money created by the company’s assets and guaranty deposits.
- States establish coverage limits on claims (e.g., $300,000 for property and liability claims).
- Policyholders can sue the insurance company’s estate if the claim exceeds the state guaranty coverage.
Use an independent agent
They might seem inconsequential, but insurance ratings matter. Before you decide on an insurance company, look at its financial ratings. Ask your independent insurance agent for the latest ratings on the companies they propose if they haven’t included them in your quote comparison. They’ll help you choose the best company for your insurance needs.